The Importance of Carbon Monoxide Sensors in Generators: A Critical Safety Measure
In recent years, the United States has taken significant steps to enhance public safety by mandating that generators be equipped with carbon monoxide (CO) sensors. This measure is part of a broader initiative to reduce the risks associated with the use of portable generators, particularly the dangers posed by carbon monoxide poisoning. Carbon monoxide is an odorless, colorless gas that can be deadly when inhaled in large quantities. The combination of generators and carbon monoxide sensors represents a critical development in ensuring the safety of users, particularly during power outages or in areas with limited ventilation.
This article explores the importance of carbon monoxide sensors in generators, the legislative background behind the mandate, how these sensors work, and the broader implications for public safety.
Understanding the Dangers of Carbon Monoxide
What is Carbon Monoxide?
Carbon monoxide (CO) is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas produced by burning fossil fuels such as coal, oil, natural gas, wood, and propane. Because it is undetectable by human senses, it is often referred to as a "silent killer." When inhaled, carbon monoxide can interfere with the body's ability to transport oxygen, leading to serious health effects and, in extreme cases, death.
Health Risks Associated with Carbon Monoxide Exposure
When carbon monoxide is inhaled, it binds to hemoglobin in the blood, forming carboxyhemoglobin (COHb), which reduces the blood's oxygen-carrying capacity. This can lead to symptoms such as:
- Mild Exposure: Headache, dizziness, confusion, nausea, and shortness of breath.
- Moderate Exposure: Chest pain, impaired judgment, blurred vision, and reduced coordination.
- Severe Exposure: Loss of consciousness, seizures, brain damage, and death.
Prolonged exposure to even low levels of carbon monoxide can be harmful, and high levels can cause death within minutes. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), more than 400 Americans die each year from unintentional carbon monoxide poisoning, and thousands more are hospitalized.
Carbon Monoxide Poisoning and Generators
Portable generators are a common source of carbon monoxide poisoning, particularly during power outages when they are used indoors or in enclosed spaces like garages, basements, or near windows. The internal combustion engines in generators produce large amounts of carbon monoxide, and without proper ventilation, the gas can quickly accumulate to dangerous levels.
Many tragic incidents have been reported where individuals were overcome by carbon monoxide from generators, often without realizing they were in danger. These incidents highlight the need for greater awareness and the implementation of safety measures, such as the installation of carbon monoxide sensors.
Legislative Background: The U.S. Mandate for Carbon Monoxide Sensors in Generators
The Consumer Product Safety Improvement Act (CPSIA)
The U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) has been at the forefront of efforts to reduce carbon monoxide poisoning from portable generators. One of the key legislative developments in this area is the Consumer Product Safety Improvement Act (CPSIA), which was passed in 2008. While the CPSIA primarily addresses the safety of children's products, it also empowers the CPSC to set safety standards for a wide range of consumer products, including generators.
CPSC Regulations on Portable Generators
In response to the increasing number of carbon monoxide poisoning incidents, the CPSC has introduced regulations specifically targeting portable generators. These regulations require manufacturers to incorporate technology that significantly reduces the risk of carbon monoxide poisoning. One of the most critical aspects of these regulations is the mandate for carbon monoxide sensors in generators.
The regulations specify that portable generators sold in the United States must include an integrated carbon monoxide detection system that automatically shuts off the generator when CO levels reach a dangerous threshold. This safety feature is designed to prevent the buildup of carbon monoxide in enclosed spaces, thereby reducing the risk of poisoning.
Impact of the Mandate
The mandate for carbon monoxide sensors in generators represents a significant step forward in protecting public health and safety. By ensuring that all portable generators are equipped with CO sensors, the regulations aim to reduce the number of carbon monoxide-related injuries and fatalities. This mandate also places the responsibility on manufacturers to innovate and develop safer products for consumers.
How Carbon Monoxide Sensors Work
Basic Principles of Carbon Monoxide Detection
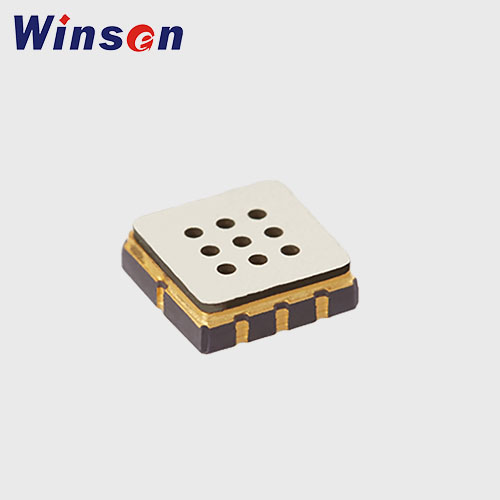
Carbon monoxide sensors operate on various principles, but the most common types used in generators are electrochemical sensors. These sensors detect carbon monoxide through a chemical reaction that produces an electrical current proportional to the concentration of CO in the air.
Electrochemical Sensors
Electrochemical sensors are widely used in carbon monoxide detectors due to their accuracy, sensitivity, and reliability. The sensor consists of a chamber filled with an electrolyte solution and electrodes. When carbon monoxide enters the chamber, it reacts with the electrolyte, generating an electrical current. The strength of this current is directly related to the concentration of carbon monoxide in the environment.

| Target: | CO |
| Model: | ME2-CO-Φ14x5 |
| Detection range: | 0~1000ppm |
| Detection principle: | Electrochemical |
| Characteristics: | Low consumption,High precision |
| Resolution and accuracy: | >0.8nA/ppm |
| Response time: | <30S |
ME2-CO-Φ14x5 Manual download
Get Price Whatsapp
Other Types of Carbon Monoxide Sensors
While electrochemical sensors are the most common, other types of carbon monoxide sensors include
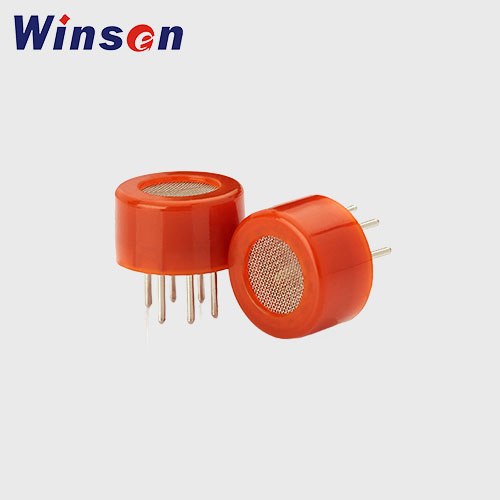
Metal Oxide Semiconductor (MOS) Sensors
These sensors detect carbon monoxide by measuring changes in the electrical resistance of a metal oxide when exposed to CO. MOS sensors are durable and can operate in harsh environments but may require higher power consumption and have slower response times compared to electrochemical sensors.

MP-9 CO/CH4 Semiconductor Flat Surfaced Gas Sensor
- CO,CH4
- 50-1000ppm(CO),300-10000ppm(CH4)
- Read More
Integration of Carbon Monoxide Sensors in Generators
The integration of carbon monoxide sensors in generators involves several key components
Sensor Module: The CO sensor module is responsible for detecting carbon monoxide levels in the generator's environment. It continuously monitors the air for the presence of CO and sends signals to the generator's control system.

| Target: | Carbon Monoxide Gas |
| Model: | ZE730-CO |
| Detection range: | 0~1000ppm |
| Detection principle: | Electrochemical |
| Characteristics: | High temperature resistance, fast response, low power consumption, high precision, long life |
| Response time: | <40s |
ZE730-CO Manual download
Get Price Whatsapp
Control System: The control system processes the signals from the CO sensor. If the sensor detects that carbon monoxide levels have reached a dangerous threshold, the control system automatically shuts off the generator to prevent further CO production.
Alarm System: In addition to shutting off the generator, the control system may also trigger an audible or visual alarm to alert users to the presence of carbon monoxide. This ensures that users are aware of the potential danger and can take appropriate action.
User Interface: Some generators are equipped with a user interface that displays information about carbon monoxide levels, providing users with real-time data and warnings.
Conclusion
The integration of carbon monoxide sensors in generators represents a significant advancement in consumer safety and public health. As part of a broader legislative effort to reduce the risks associated with portable generators, these sensors provide a critical safeguard against carbon monoxide poisoning, a silent and deadly threat.
By automatically shutting off generators when dangerous levels of CO are detected, these sensors prevent the buildup of the gas in enclosed spaces, protecting users and saving lives. The mandate for carbon monoxide sensors in generators is not only a regulatory requirement but also a reflection of the growing awareness of the importance of safety in everyday products.
As technology continues to evolve, the combination of generators and carbon monoxide sensors will remain a vital tool in ensuring the safety and well-being of individuals and families who rely on these devices. Whether during power outages, in remote locations, or in emergency situations, the presence of a carbon monoxide sensor in a generator can make the difference between life and death.