Electrochemical CO Sensors: Working Principle, Design, and Applications
1. Introduction
Carbon monoxide (CO) is a toxic, colorless, and odorless gas that poses serious health risks when inhaled, making reliable CO detection systems essential for residential, commercial, industrial, and transportation applications. Among various gas sensing technologies, electrochemical CO sensors stand out due to their high sensitivity, accuracy, low power consumption, and compact size.
2. What is an Electrochemical Sensor?
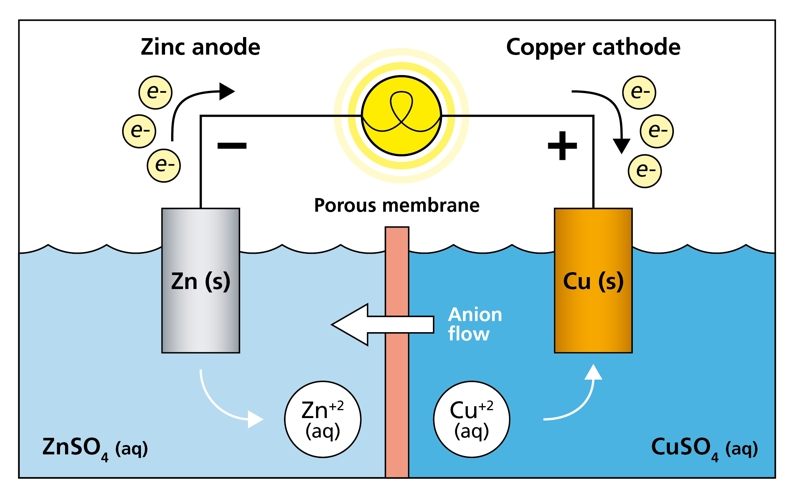
An electrochemical sensor is a chemical sensor that uses an electrochemical reaction to detect a target gas and produce an electrical signal proportional to its concentration. These sensors operate by allowing gas molecules to diffuse through a membrane and react at an electrode, leading to an electron transfer process (redox reaction) that generates measurable current.
3. Overview of Carbon Monoxide (CO)
Carbon monoxide is produced through incomplete combustion of fossil fuels. Common sources include:
- Gas heaters and furnaces
- Vehicle exhaust
- Fires and stoves
- Boilers and industrial burners
CO binds with hemoglobin in the blood, forming carboxyhemoglobin, which blocks oxygen transport and leads to symptoms such as dizziness, headaches, or even death at high concentrations.
4. What is an Electrochemical CO Sensor?
An electrochemical CO sensor is a type of gas sensor that detects carbon monoxide by means of an electrochemical cell. When CO gas enters the sensor, it undergoes a redox reaction at the sensing electrode, generating a small electrical current that is directly proportional to the CO concentration in the air.
Electrochemical CO sensors are widely used in:
- CO alarms and detectors
- Industrial safety systems
- Smart homes
- Vehicles and underground parking
- HVAC and building automation systems
5. Working Principle
The core of an electrochemical CO sensor is a three-electrode electrochemical cell consisting of:
- Working electrode (anode)
- Counter electrode (cathode)
- Reference electrode
Reaction Process:
-
Diffusion: CO diffuses through a gas-permeable membrane into the electrolyte.
-
Oxidation: CO is oxidized at the working electrode:
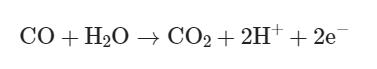
- Current Generation: The electrons generated are measured as current. The magnitude of current is directly proportional to the CO concentration.
6. Sensor Structure and Components
Main Components:
- Gas Diffusion Barrier: Controls the rate at which CO enters the cell.
- Electrolyte: Often sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) or potassium hydroxide (KOH).
- Working Electrode: Usually made of platinum or gold, catalyzes CO oxidation.
- Counter Electrode: Completes the electrochemical circuit.
- Reference Electrode: Maintains a stable voltage reference for accuracy.
- Housing and Filter: Protects against dust, humidity, and interfering gases.
Some advanced designs integrate:
- Temperature compensation circuits
- Microcontrollers
- Digital output interfaces
Winsen Electrochemical CO Sensor:

EC Hazardous Toxic Gas Detection Sensor Module ZE03
- CO,O2,NH3,H2S,NO2,O3,SO2, CL2,HF,H2,PH3,HCL, etc.
- See manual
- Read More
7. Key Specifications
| Specification | Typical Value Range |
|---|---|
| Measurement Range | 0 – 500 ppm or 0 – 1000 ppm |
| Accuracy | ±5 ppm or ±5% of reading |
| Resolution | 1 ppm |
| Response Time (T90) | <30 seconds |
| Operating Temperature | –20°C to +50°C |
| Operating Humidity | 15% – 90% RH (non-condensing) |
| Output Signal | Analog (μA), I²C, UART, or digital |
| Power Consumption | Very low (typically <10 mW) |
| Lifespan | 2 – 5 years |
8. Performance Characteristics
- High Selectivity: Electrochemical cells are selective to CO and less prone to interference from other gases.
- Long-Term Stability: Maintains sensitivity and accuracy over months to years.
- Linear Output: Signal is linearly proportional to CO concentration.
- Low Drift: Typically <5% per year.
9. Advantages of Electrochemical CO Sensors
Highly accurate and sensitive
Compact and lightweight
Low power consumption (ideal for battery-powered devices)
Wide operating range
Stable performance in varying temperatures and humidity
Good selectivity with minimal cross-gas interference
No external power needed for sensing element
10. Limitations and Challenges
Limited lifespan (typically 2–5 years)
Sensitive to high humidity or condensation
Calibration required over time
May be affected by hydrogen in some environments
Electrolyte leakage if damaged or exposed to extreme conditions
Temperature compensation is needed for precise results in dynamic environments
11. Applications
Residential and Commercial
- CO alarms in homes, hotels, schools
- Smart home gas monitoring systems
Industrial Safety
- Confined space entry monitoring
- Boiler rooms and engine rooms
- Chemical manufacturing
Automotive and Transport
- Cabin air quality monitoring
- Underground parking garages
- Subway and tunnel systems
HVAC Systems
- Demand-controlled ventilation (DCV)
- Integration into building management systems (BMS)
Medical and Laboratory
- Monitoring in oxygen therapy rooms
- Laboratory environments with combustion processes
12. Comparison with Other CO Sensor Types
| Feature | Electrochemical | Semiconductor (MOS) | NDIR |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | High | Moderate | High |
| Power Consumption | Low | High | Moderate |
| Size | Small | Small | Medium |
| Selectivity | High | Low (prone to interference) | High |
| Cost | Moderate | Low | High |
| Lifespan | 2–5 years | 5–10 years | 5–10 years |
| Output Type | Analog/Digital | Resistance-based | Optical |
| Use Case | Alarms, detectors | Air quality, warning | Industrial systems |
13. Calibration and Maintenance
Calibration
- Regular calibration with known CO concentrations ensures accuracy.
- Use zero gas and span gas to adjust sensor readings.
- Calibrate every 6 to 12 months, or as per manufacturer's recommendation.
Maintenance Tips
- Keep away from water and solvents
- Avoid prolonged exposure to high CO levels
- Store in dry, sealed containers if unused
- Replace sensor after expiration date
14. Integration in Modern Systems
Electrochemical CO sensors can be easily embedded into:
- IoT devices (Wi-Fi, Zigbee, NB-IoT)
- Microcontroller boards (Arduino, Raspberry Pi)
- Industrial control systems (PLC, SCADA)
- Battery-powered portable detectors
Common output interfaces:
- Analog voltage or current
- I²C / UART / Modbus RTU
- 4–20 mA or 0–10V for industrial controllers
15. Standards and Compliance
| Standard | Region / Organization | Application |
|---|---|---|
| UL 2034 | United States | CO alarms for residential use |
| EN 50291 | European Union | Domestic CO alarm performance |
| CSA 6.19 | Canada | CO alarm standard |
| ISO 18158 | International | Workplace exposure monitoring |
| OSHA PEL | USA (Occupational Safety) | 50 ppm over 8 hours |
| NIOSH REL | USA Health Standards | 35 ppm over 8 hours |
Make sure your product meets local certification requirements before sale or integration.
16. Emerging Trends and Future Developments
Ultra-low power CO sensors for wearables
Mobile app integration for real-time CO alerts
AI and machine learning for predictive CO level analysis
Cloud connectivity for large-scale CO monitoring in smart cities
Miniaturized MEMS-based electrochemical sensors
Multi-gas sensor modules integrating CO with VOC, NO₂, or O₃ detection
17. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: How accurate are electrochemical CO sensors?
Most high-quality models offer accuracy of ±5% of reading or better under standard conditions.
Q2: What is the typical lifespan of an electrochemical CO sensor?
About 2 to 5 years, depending on the operating environment and usage.
Q3: Do these sensors require calibration?
Yes. Calibration is needed every 6–12 months for optimal performance.
Q4: Can electrochemical CO sensors be used outdoors?
Generally designed for indoor or sheltered environments; outdoor use may require weatherproof housing.
Q5: Are electrochemical sensors affected by other gases?
They are selective, but hydrogen and ethanol may interfere if present in high concentrations.
18. Conclusion
Electrochemical CO sensors are a crucial technology for detecting carbon monoxide across a wide range of applications, from residential safety to industrial automation. Offering high accuracy, selectivity, and energy efficiency, they are the preferred solution for compact, reliable, and real-time CO detection.
As technology advances, we expect further integration into IoT systems, better miniaturization, and AI-enhanced gas analysis, making electrochemical CO sensors even more vital in our increasingly connected and safety-conscious world.