NH₃ & H₂S Gas Monitoring in Smart Livestock Farming - Winsen ZE03 Sensor Solutions for Korea
The agricultural industry is undergoing a rapid digital transformation, and South Korea has positioned itself as a regional leader in smart livestock farming. Traditional livestock management, heavily dependent on manual labor and basic ventilation, is giving way to intelligent systems powered by the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and sensor-based monitoring. Among the most pressing issues in modern farms are the air quality challenges posed by harmful gases such as ammonia (NH₃) and hydrogen sulfide (H₂S).
These gases, often generated from animal waste decomposition and poor ventilation, are not only toxic to animals but also pose serious risks to farm workers and nearby communities. Prolonged exposure to high concentrations can reduce productivity, compromise animal welfare, and even lead to fatal incidents in poorly managed barns.
Recognizing these challenges, Winsen—a global sensor technology leader—has developed the ZE03 series modular gas sensor platforms, which provide accurate, reliable, and cost-effective detection of multiple gases, including ammonia (NH₃) and hydrogen sulfide (H₂S). This makes the ZE03 series especially suitable for Korean smartfarming applications, where regulatory compliance, animal welfare, and economic efficiency are critical.
2. The Challenges of Smart Livestock Farming
2.1 Ammonia (NH₃) Hazards in Livestock Farms
Ammonia is one of the most common and problematic gases in animal husbandry. It is produced through the microbial decomposition of urea in manure and urine. Concentrations in enclosed barns can easily reach harmful levels, especially in pig farms and poultry houses where waste management is difficult.
Health impacts on animals:
- Respiratory irritation: Ammonia damages the mucous membranes in animals, leading to coughing, sneezing, and chronic respiratory disease.
- Reduced growth and productivity: Studies show that broilers exposed to 50 ppm NH₃ have lower weight gain and feed efficiency.
- Egg quality decline: In poultry, ammonia exposure leads to thinner eggshells and lower production rates.
- Stress and behavior changes: Prolonged exposure results in increased stress hormones, reducing overall health.
Health impacts on humans:
- Farm workers exposed to ammonia levels above 25 ppm (OSHA standard) may suffer eye and throat irritation.
- At 50–100 ppm, prolonged exposure can cause chronic respiratory diseases.
- Above 300 ppm, ammonia exposure is life-threatening.
In South Korea, where pig and poultry farming is highly intensive, ammonia is a leading cause of odor complaints from nearby residents and a key target for environmental regulations.
2.2 Hydrogen Sulfide (H₂S) Hazards in Livestock Farms
Hydrogen sulfide is another extremely dangerous gas, often called a “silent killer” in livestock environments. It is released from the anaerobic decomposition of manure, especially in slurry pits and lagoons.
Health impacts on animals:
- Even low concentrations (10–20 ppm) can stress livestock.
- Exposure above 50 ppm can cause nervous system disruption and death.
- Animals confined in poorly ventilated barns are at the highest risk.
Health impacts on humans:
- 0–10 ppm: Detectable rotten-egg smell; irritation of eyes and throat.
- 20–50 ppm: Severe eye damage, respiratory issues, headaches.
- 100–150 ppm: Loss of smell (olfactory paralysis), making detection impossible without sensors.
- 300–500 ppm: Rapid unconsciousness, respiratory paralysis, death.
Korea has seen multiple cases of fatal accidents in manure pits due to H₂S exposure. This has made continuous monitoring of hydrogen sulfide mandatory in advanced farm management practices.
2.3 Combined Effects of NH₃ and H₂S
The challenge in farms is that NH₃ and H₂S often coexist. While ammonia typically irritates respiratory systems, hydrogen sulfide causes acute toxicity. Together, they create a synergistic health risk:
- Animals already weakened by ammonia irritation are less resistant to hydrogen sulfide poisoning.
- Workers cannot rely on smell because prolonged ammonia exposure dulls olfactory sensitivity, while H₂S quickly paralyzes the sense of smell at dangerous levels.
- Both gases contribute to corrosion of farm equipment, increasing maintenance costs.
Thus, Korean smart farms require a dual-gas monitoring solution, not just single-gas sensors.
2.4 Environmental and Economic Impacts
Beyond direct health risks, NH₃ and H₂S emissions contribute to broader environmental and economic issues:
- Air pollution: Ammonia contributes to fine particulate matter (PM2.5), worsening urban air quality.
- Odor complaints: Community opposition to farms in Korea often centers on odor, linked to both NH₃ and H₂S.
- Regulatory penalties: Farms exceeding emission limits risk government fines and closures.
- Reduced productivity: Poor air quality leads to lower feed conversion ratios, reduced milk yield, and slower growth.
In short, gas monitoring is not optional; it is essential for profitability and compliance in Korean livestock operations.
3. Gas Sensors in Modern Farming
3.1 Role of IoT and Smart Sensors
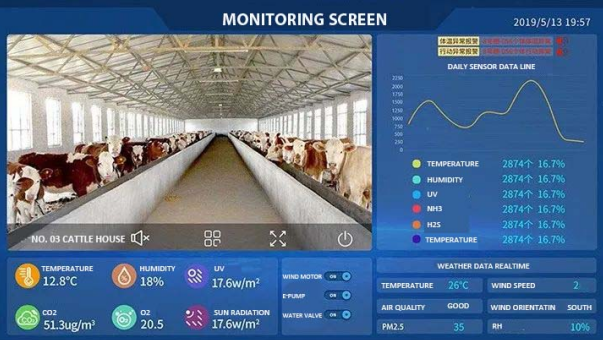
Smart livestock farming relies on continuous data collection from multiple environmental parameters, including:
- Temperature
- Humidity
- CO₂
- NH₃
- H₂S
- Dust levels
By integrating gas sensors with IoT platforms, farmers can:
- Automatically trigger ventilation systems when gas levels exceed thresholds.
- Log data for regulatory reporting.
- Use AI analytics to predict risks before they escalate.
- Reduce labor costs through remote monitoring.
Gas sensors thus form the backbone of precision livestock farming (PLF).
3.2 Current Market in Korea
South Korea has invested heavily in smart farming initiatives through programs like the Smart Farm Innovation Valley. The livestock sector is a priority, especially given the social pressure to reduce odor pollution and improve animal welfare.
- Pig farming: Over 6,000 pig farms in Korea face strict odor and emission regulations.
- Poultry farming: Intensive broiler and layer houses are adopting smart sensors to optimize ventilation.
- Cattle farms: Although ammonia levels are lower, hydrogen sulfide from manure lagoons remains a risk.
The demand for multi-gas sensor modules is rapidly increasing, especially ones that can be easily integrated into existing IoT platforms.
4. Winsen ZE03 Sensor Module
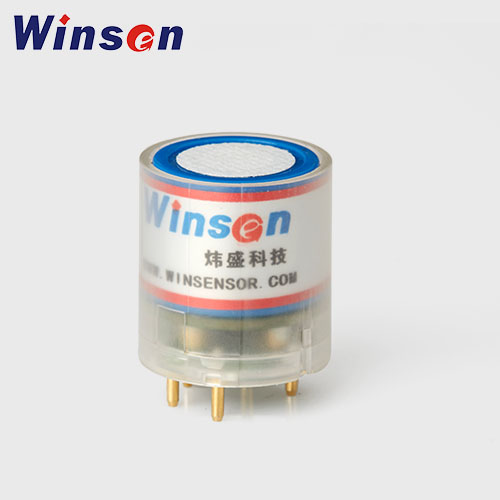

| Target: | CO,O2,NH3,H2S,NO2,O3,SO2, CL2,HF,H2,PH3,HCL, etc. |
| Model: | ZE03 |
| Detection range: | See manual |
| Detection principle: | Module, electrochemical |
| Characteristics: | Supply UART output and analog voltage output; Use for portable and fixed gas detector, various gas detection equipment and occasion. |
| Size: | ø23.5mm*24.5mm |
| Working conditions: | See manual |
ZE03 Manual download
Get Price Whatsapp
This principle ensures:
- High selectivity (different membranes for different gases).
- Linear response over the detection range.
- Low cross-sensitivity compared to cheaper semiconductor sensors.
- Stability in varying farm conditions (temperature, humidity).
4.1 Key Features for Livestock Applications
- Factory Calibration: ZE03 sensors come pre-calibrated, reducing on-site setup effort.
- Temperature & Humidity Compensation: Built-in correction algorithms ensure stable readings in barns where humidity often exceeds 80%.
- Fast Response Time: Response within 30 seconds ensures real-time control of ventilation.
- Long Service Life: Electrochemical sensing elements typically last 2–3 years under normal farm conditions.
- Low Power Consumption: Suitable for wireless IoT nodes deployed in barns.
- Compact Size: Can be installed in multiple points for distributed monitoring.
4.2 Advantages of ZE03 Over Alternatives
| Feature | ZE03 Sensor | Semiconductor Sensor | Infrared Sensor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Selectivity | High | Low (many false alarms) | Medium |
| Accuracy | ±5% | ±20% | ±10% |
| Cost | Moderate | Low | High |
| Lifetime | 2–3 years | 1–2 years | 5+ years |
| Response Time | <30s | 1–2 min | <10s |
| Suitability for NH₃/H₂S | Excellent | Poor | Limited |
ZE03 strikes the balance between accuracy and affordability, making it ideal for Korean farms where budget and performance must align.
5. Benefits of ZE03 for the Korean Livestock Industry
Smart livestock farming in Korea is driven by three pillars: animal welfare, environmental sustainability, and farm profitability. The Winsen ZE03 sensor directly supports all three pillars by delivering reliable NH₃ and H₂S monitoring.
5.1 Improved Animal Welfare
Livestock productivity is closely linked to air quality inside barns. Even moderate ammonia levels can reduce feed efficiency and increase disease incidence.
Key Benefits for Animals:
- Better respiratory health: Continuous monitoring ensures NH₃ stays below the welfare threshold of 20 ppm recommended by Korean authorities.
- Reduced stress: Animals exposed to clean air show improved behavior, lower stress hormone levels, and higher reproductive success.
- Higher productivity: Pigs and poultry gain more weight with the same feed when ammonia levels are controlled.
- Lower mortality: Hydrogen sulfide monitoring prevents fatal exposure during manure management.
By integrating ZE03 sensors, Korean farmers can achieve healthier herds and flocks, directly translating into higher yields.
5.2 Compliance with Korean Regulations
South Korea has progressively tightened regulations on farm odors, emissions, and worker safety. Farms exceeding ammonia or hydrogen sulfide thresholds risk fines, legal disputes, or even forced closure.
- Ammonia: Recognized as a major contributor to fine dust (PM2.5), Korea’s Ministry of Environment enforces emission control measures.
- Hydrogen sulfide: Classified as an industrial toxic gas, with occupational exposure limits of 10 ppm (8-hour TWA).
5.3 Reduction of Odor & Environmental Pollution
Odor pollution is one of the most sensitive issues in Korean farming. Rural communities increasingly resist the expansion of pig and poultry farms due to offensive smells, mainly caused by NH₃ and H₂S.
By deploying ZE03 sensors, farms can:
- Continuously measure odor-related gases.
- Optimize ventilation and biofilter operations.
- Demonstrate emission control efforts to local authorities.
This not only improves community relations but also supports the government’s green agriculture policies.
5.4 Worker Safety and Health
Farm workers in Korea often perform tasks in confined spaces, such as manure pits, where H₂S levels can spike dangerously. Tragic accidents have occurred due to lack of detection systems.
Benefits of ZE03 for workers:
- Early warning of toxic gas build-up.
- Personal safety devices (portable detectors using ZE03) can protect workers.
- Improved working conditions reduce absenteeism and turnover.
By protecting farm staff, ZE03 contributes to both ethical labor practices and operational stability.
5.5 Economic Efficiency and ROI
While installing gas sensors adds upfront costs, ZE03 quickly pays for itself through:
- Improved feed conversion ratio (FCR): Cleaner air reduces feed waste.
- Lower veterinary costs: Fewer respiratory illnesses.
- Better community acceptance: Avoids costly legal disputes and protests.
- Reduced equipment corrosion: NH₃ and H₂S monitoring helps schedule maintenance before damage occurs.
A study conducted on pig farms showed that NH₃ reduction improved profit margins by 5–10%, more than offsetting sensor investment costs.
5.6 Integration with Korean Smart Farm Ecosystem
Korea is building a Smart Farm Convergence Alliance, integrating universities, tech firms, and farmers. ZE03 sensors:
- Fit directly into K-Smart Farm platforms.
- Work with Korean IoT gateway manufacturers.
- Provide data for AI-driven animal health prediction models.
This ensures that ZE03 is not just a standalone device, but part of Korea’s broader agricultural innovation strategy.
5.7 Sustainability and ESG Benefits
South Korea increasingly emphasizes ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) practices in agriculture. Export-oriented farms must also meet international standards.
By adopting ZE03 sensors, farms can report:
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
- Compliance with animal welfare standards.
- Commitment to worker safety.
This strengthens their market reputation and supports sustainable branding in both domestic and export markets.
6. Key Reasons to Select ZE03 for NH₃ and H₂S Monitoring
6.1 Factory Calibration and Accuracy
Each ZE03 module undergoes factory calibration to ensure accuracy for specific gas detection. For NH₃ and H₂S:
- NH₃ range: 0–100 ppm (optional 0–500 ppm)
- H₂S range: 0–100 ppm
- Resolution: 1 ppm or better
- Response time (T90): typically < 30 seconds
This precision allows ZE03 to detect harmful concentrations before they cause stress to animals or risk to farm workers.
6.2 Modular and Flexible Integration
The ZE03 module communicates through standard UART or analog output. Farmers, system integrators, or equipment suppliers can easily:
- Embed it into ventilation controllers.
- Connect it to wireless gateways (LoRa, NB-IoT, ZigBee, Wi-Fi).
- Integrate into cloud dashboards for 24/7 monitoring.
6.3 Long-Term Stability
Electrochemical cells used in ZE03 are optimized for extended lifespan:
- 2+ years of stable operation in agricultural settings.
- Built-in temperature and humidity compensation.
- Robust design to handle fluctuating barn environments.
6.4 Cost-Effectiveness
Compared to bulky industrial analyzers, ZE03 offers a low-cost, high-value solution:
- Affordable enough for multi-point distributed sensing.
- Reduces overall system integration costs.
- Helps farmers comply with environmental laws without heavy capital investment.
6.5 Support for Korean Regulations
Korea’s livestock odor and air quality guidelines emphasize reduction of ammonia and hydrogen sulfide. By adopting ZE03, farms can:
- Prove compliance with regulatory limits.
- Avoid fines or shutdowns.
- Improve community relations by reducing odor complaints.
7. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Why is ammonia monitoring important in livestock farming?
Ammonia causes respiratory stress in animals, reduces feed efficiency, and contributes to poor growth. In humans, it causes irritation and long-term lung issues. Monitoring ensures concentration stays below harmful thresholds.
Q2: What are the risks of hydrogen sulfide in farms?
H₂S is highly toxic even at low ppm levels. Prolonged exposure can be fatal to both animals and workers. Real-time H₂S monitoring is critical for farm safety compliance.
Q3: How does ZE03 compare to traditional gas analyzers?
Traditional analyzers are large, expensive, and require trained staff. ZE03 is compact, affordable, and designed for distributed, automatic monitoring. This makes it ideal for smart farming networks.
Q4: What communication options are available with ZE03?
ZE03 offers UART (TTL) and analog voltage output. It can easily connect to IoT gateways that support Wi-Fi, LoRa, NB-IoT, ZigBee, or 4G/5G.
Q5: How often does ZE03 need calibration?
Factory calibration ensures long-term stability. However, for best accuracy in farm conditions, a 6–12 month verification is recommended.
Q6: Can ZE03 withstand high humidity in barns?
Yes. ZE03 modules are designed with temperature and humidity compensation. With proper installation (protective housing), they function reliably in humid barns.
Q7: Is ZE03 suitable for Korean government-supported smart farm programs?
Yes. ZE03’s modular integration and affordability make it compatible with smart farm initiatives promoted by Korea’s Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs.
Q8: What maintenance is required?
Minimal. Periodic inspection, occasional calibration check, and ensuring dust/ventilation filters remain unclogged.
Q9: Can ZE03 detect other gases besides NH₃ and H₂S?
Yes. The ZE03 series supports multiple gas detection modules including CO₂, CO, CH₄, O₂, and VOCs — making it versatile for broader farm applications.
Q10: Where can Korean farmers purchase ZE03?
Winsen works with global distributors and can also directly support Korean integrators and smart farming solution providers.