Perceiving Every Pa of Change! Winsen Technology Pressure Sensors Ensure Gas Supply System Safety
When natural gas awakens from deep underground reservoirs or distant LNG terminals, it begins a long journey—spanning hundreds of kilometers, undergoing multiple pressure transformations. Throughout this journey, precision pressure monitoring and control play a vital role in ensuring the system's safety, stability, and efficiency.
Gas Supply Systems: A Complex and Critical Journey
The modern gas supply system consists of three parts: source, distribution system, and users, forming a typical “source—network—load” collaborative system.
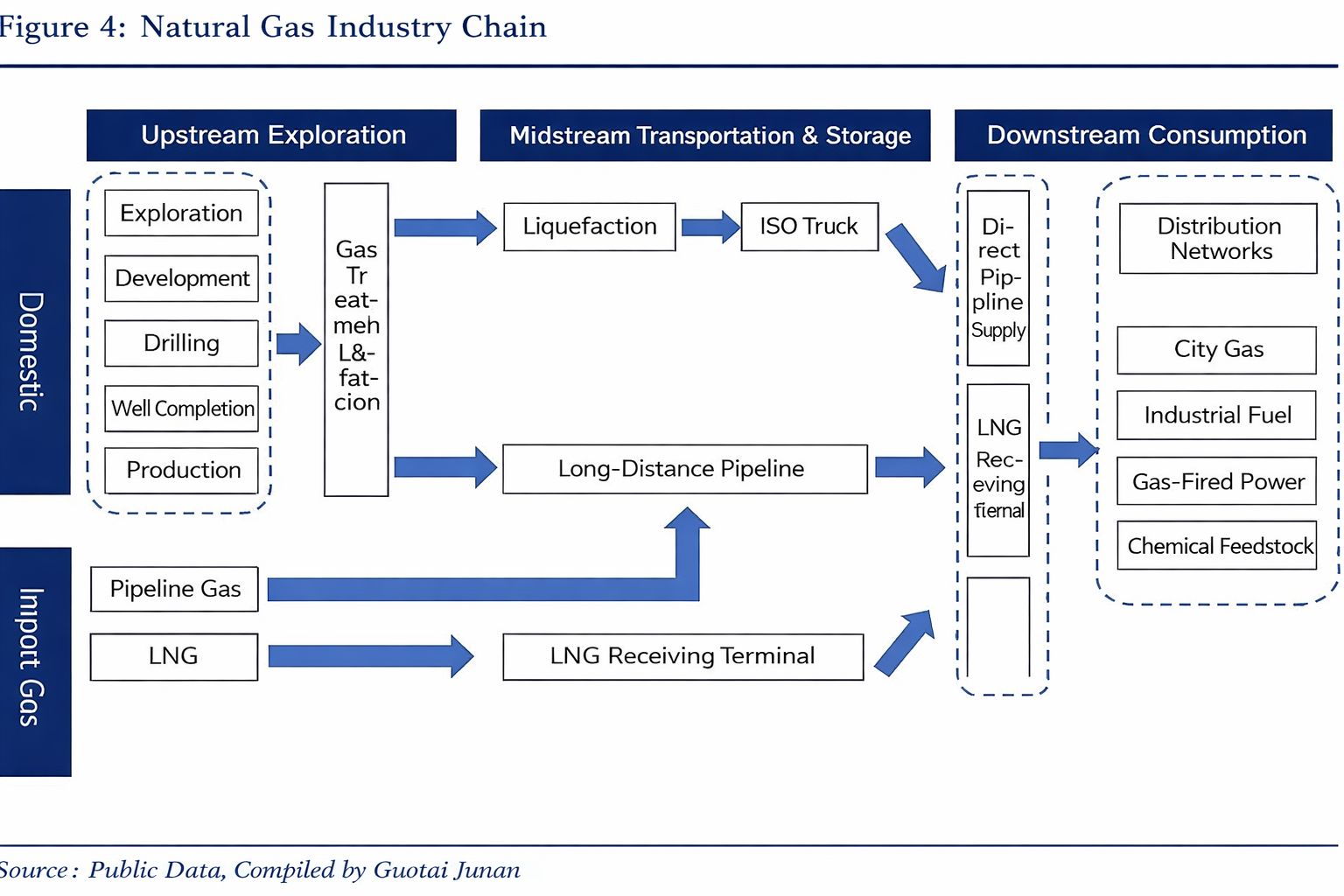
- Gas Source: Gas enters cities under high pressure, typically through natural gas metering stations or LNG regasification terminals.
- Gas Storage & Regulation: Gas storage facilities regulate supply-demand peaks.
- Gas Distribution Network: Gas is transported through various pressure levels (high, medium, and low pressure) to consumers.
- Final Delivery: Gas enters homes and businesses through pipelines connected to meters, stoves, and heaters.
The process involves gradual pressure reduction, from high-pressure source to low-pressure end-user. Precision sensing and control of this pressure drop is essential to ensuring safe and efficient gas delivery.
Pressure Sensors as the Watchful Guardians of Gas Safety
Pressure sensors are the vigilant sentinels deployed at every key point of pressure conversion and monitoring in this complex system. Their mission evolves dynamically as gas travels from source to user.
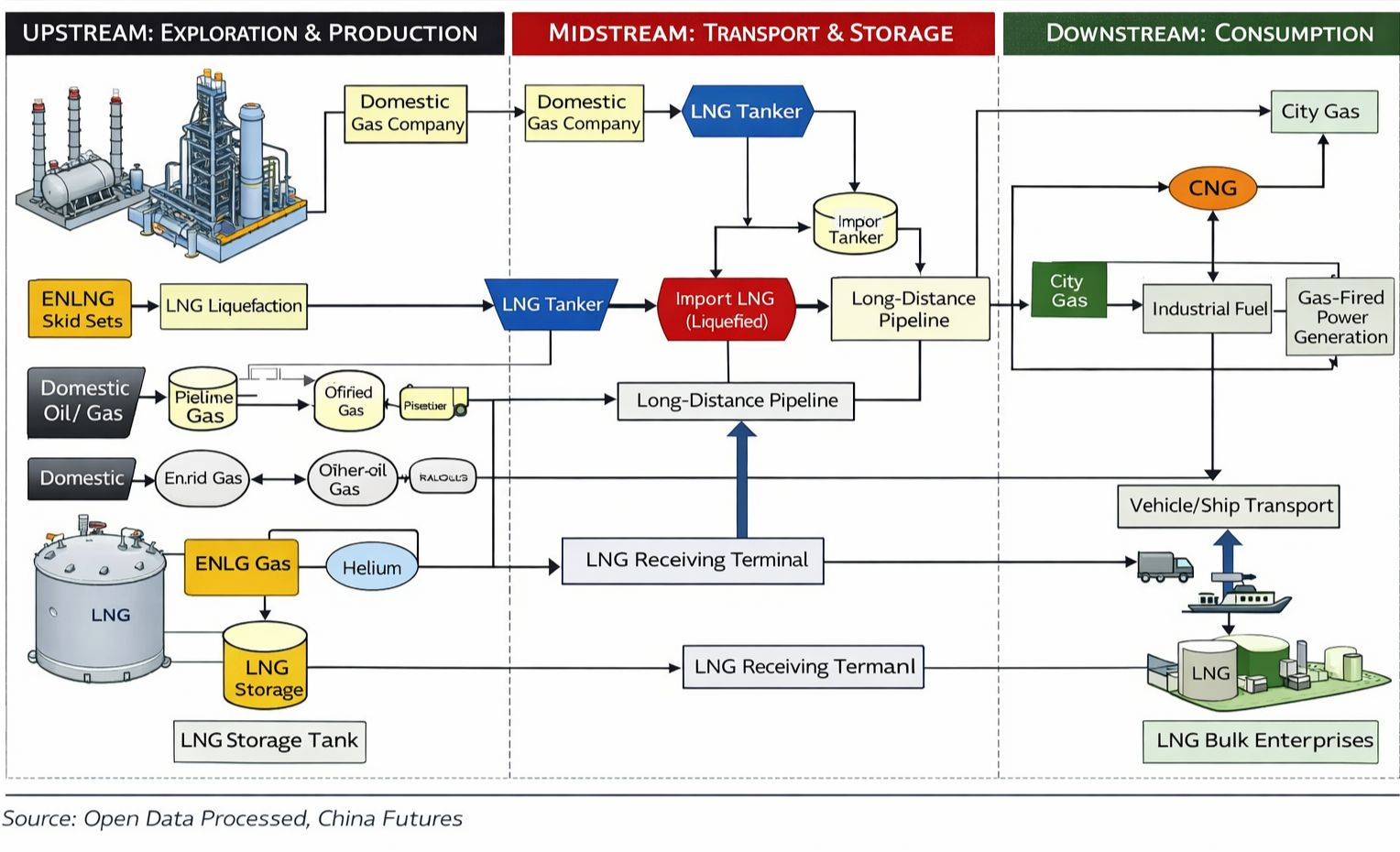
At the Gas Source
At the storage tanks, metering stations, and gas filling stations, pressure sensors play a crucial role in ensuring gas pressure remains within safe limits before entering the pipeline and providing fundamental flow regulation.
Pressure Monitoring:
Sensors continuously monitor the entry pressure of storage tanks and high-pressure pipelines. Data is fed into regulation equipment to ensure the pressure entering the pipeline network conforms to design specifications, typically 0.2–0.5 MPa, preventing pipeline rupture due to overpressure or supply interruptions due to underpressure.
Safety Warnings:
When abnormalities arise—such as low liquid levels inside storage tanks causing sudden pressure drops, or high temperatures leading to increased pressure—sensors trigger alarm systems and automatic shut-off valves to prevent accidents from escalating.
In-Depth Pressure Monitoring Across the Distribution Network
Once gas enters the city’s distribution network, pressure sensors are strategically placed across key nodes in the regulating stations, branch distribution points, and pipelines to monitor flow, ensure safety, and improve efficiency.
Pressure Gradient Monitoring
Gas pressure decreases due to friction and flow velocity changes. Sensors distributed along pipelines and pressure regulating stations continuously measure local pressure (gauge pressure, absolute pressure, or differential pressure). By monitoring the pressure drop, they calculate gas flow and transport efficiency.
Leak Detection
Even slight pressure drops can indicate gas leaks in the pipeline. Pressure sensors can detect these minor changes, triggering valve closures or alarm systems to prevent gas leakage and ensure safety.
Smart Scheduling and Integration with SCADA Systems
In smart gas distribution networks, sensors provide real-time data to SCADA systems, enabling optimized control of valve adjustments. This allows gas to be evenly distributed across regions and further optimizes energy use.
At the User Terminal: Ensuring Safety and Accurate Measurement
Pressure sensors are also embedded in gas meters, home gas stoves, and gas detectors to ensure:
- Accurate measurement of gas flow and volume
- Safety by detecting minor pressure fluctuations caused by potential leaks
Gas Metering
In smart gas meters, pressure sensors work alongside temperature sensors to compensate for changes in gas density and volume, ensuring accurate readings regardless of temperature variations.
Leak Detection in Homes
By monitoring even slight pressure drops in household pipes, sensors can detect slow gas leaks and signal early warnings, preventing potential hazards before they escalate.
Pressure Sensors in Industrial and Commercial Applications
For industrial and commercial users, precise pressure data is critical to optimizing combustion efficiency and reducing energy consumption. By closely monitoring and adjusting gas flow, pressure sensors help reduce fuel waste and improve overall energy management.
The Role of Pressure Sensors in the Entire Gas Supply Chain
From the high-pressure gas source to the multi-stage distribution network and down to the end-user, pressure sensors form a precise and reliable sensing network that protects the pipeline infrastructure, enhances the efficiency of the gas supply system, and safeguards the rights and safety of the end-users.
Pressure sensors go beyond simple installations—they are based on a deep understanding of system operating conditions, safety requirements, and long-term operations. Choosing the right pressure sensors is the first step in building a reliable and efficient sensing network.
Types of Pressure Sensors: Factors to Consider
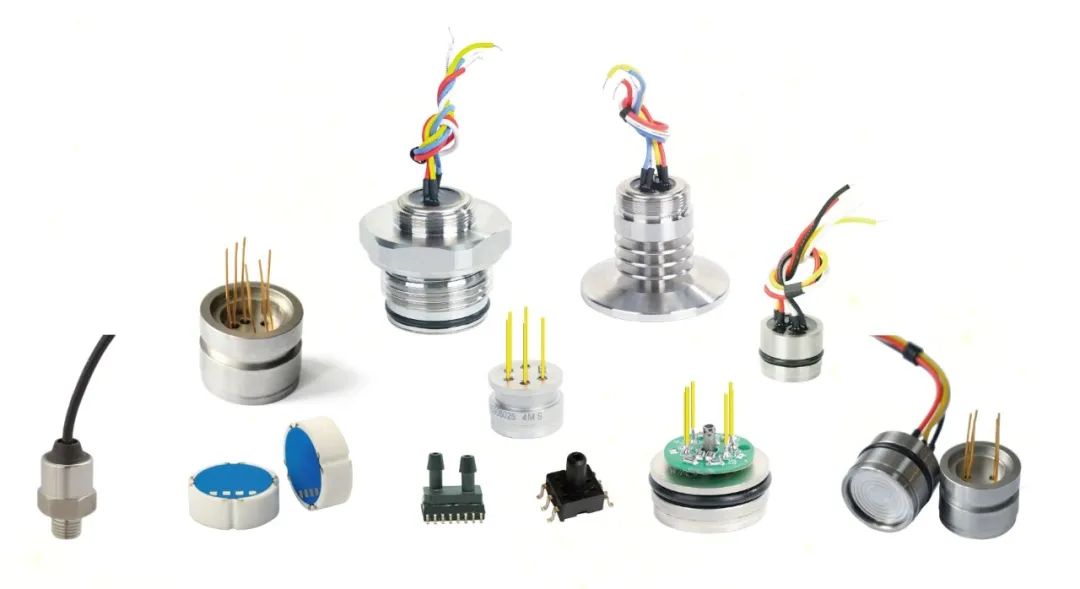

When selecting pressure sensors for different stages of the gas supply system, various factors need to be considered:
- Pressure type: gauge, absolute, or differential
- Pressure range: appropriate to the working conditions
- Accuracy: to ensure reliable measurements
- Environmental conditions: temperature, humidity, vibration, etc.
In the following sections, we will explore the role of pressure sensors in key areas, including high-pressure transmission, regulating stations, and intelligent metering systems, unveiling the full landscape of this silent protector.
FAQ
Q1: What types of pressure sensors are used in gas supply systems?
Pressure sensors can be gauge, absolute, or differential types, depending on the monitoring point and application requirements. Common applications include gas meters, pipeline pressure monitoring, and regulating stations.
Q2: How do pressure sensors help in gas leak detection?
Pressure sensors continuously monitor pressure changes in the gas distribution system. Any slight drop in pressure may signal a leak in the pipeline, triggering alarm systems and shutting off valves to prevent further escalation.
Q3: How accurate are Winsen pressure sensors?
Winsen pressure sensors offer high precision in monitoring and provide real-time data to optimize system performance, reduce energy waste, and enhance safety across the gas supply chain.
Conclusion
Pressure sensors in gas supply systems form an integral part of the safety, efficiency, and reliability of the entire pipeline infrastructure. These sensors not only ensure precise pressure control but also provide critical real-time data to prevent accidents, optimize gas distribution, and improve energy efficiency. Proper selection and deployment of pressure sensors ensure that the gas supply network remains safe, stable, and cost-effective.